What Is A Recession?
Official Recession Definition
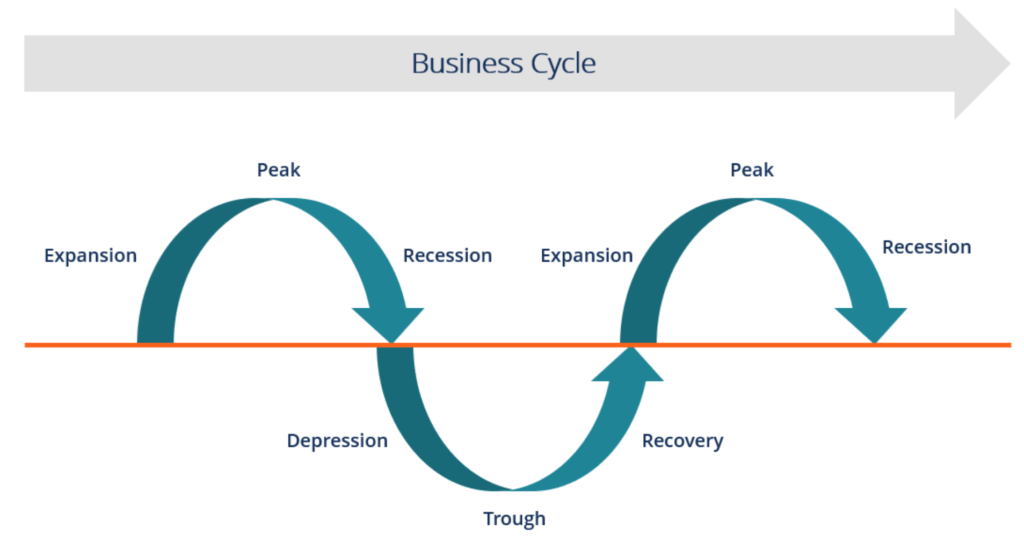
Recessions and the Business Cycle
During the expansion phase, the economy is growing and businesses are thriving. This is typically characterized by low unemployment, rising incomes, and increasing consumer spending. However, as the economy continues to grow, it eventually reaches a peak, at which point it begins to slow down. This is followed by the contraction phase, also known as a recession when the economy is declining and businesses are struggling. Finally, the economy reaches a trough, which marks the end of the recession and the beginning of a new expansion phase.
A depression, on the other hand, is a much more severe and prolonged economic downturn. It is typically defined as a period of a sustained and significant decline in economic activity, lasting several years or even longer. Depressions are typically characterized by high levels of unemployment, falling prices, and a sharp decline in consumer spending and investment.
The Great Depression of the 1930s was the most severe depression in modern history, lasting for more than a decade and causing widespread economic hardship around the world. By comparison, most modern recessions are relatively mild and do not last for more than a few years.
The Great Depression
The Great Depression began with the stock market crash of 1929, which wiped out millions of dollars of wealth and set off a chain reaction of economic events. As consumers and businesses cut back on their spending, many companies were forced to lay off workers, leading to a sharp rise in unemployment. The economy continued to decline, and by 1933, unemployment had reached 25% in the United States and many other countries around the world.
The Great Depression had far-reaching effects, not just on the economy but on society as a whole. It led to widespread poverty, political upheaval, and social unrest. Governments around the world responded with a variety of policies, including increased government spending, currency devaluation, and trade protectionism, but these measures did not quickly end the depression. It was not until the onset of World War II that many economies began to recover from the depression.
How Long Do Recessions Last?
On average, recessions in the United States have lasted for about 11 months, according to data from the National Bureau of Economic Research. However, the duration of a recession can vary depending on the specific cause of the downturn and the policies that are implemented to address it.
For example, the Great Recession of 2007-2009, which was triggered by the global financial crisis, lasted for 18 months, making it one of the longest recessions in modern history. By contrast, the recession that began in February 2020, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, lasted for just eight months, making it one of the shortest recessions on record.
Can You Predict a Recession?
It is difficult to predict a recession with certainty, as there are many factors that can affect the economy and cause it to slow down. However, there are certain indicators that can give economists and policymakers a sense of the direction in which the economy is heading.
For example, economists may look at indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, consumer spending, and the housing market to gauge the health of the economy and identify potential risks. Additionally, financial market trends, such as changes in stock prices or interest rates, can also provide insight into the likelihood of a recession.
While these indicators can be useful for detecting potential risks, it is important to remember that they are not always accurate, and there is no foolproof way to predict a recession with certainty. Ultimately, the occurrence of a recession is influenced by a wide range of factors, and it can be difficult to anticipate with precision.
How Does a Recession Affect Me?
A recession can have a number of different effects on individuals, depending on their specific circumstances. Some of the ways that a recession can impact individuals include:
- Reduced income or job loss: During a recession, businesses may experience reduced demand for their products and services, leading to layoffs and other cost-cutting measures. This can result in reduced income for workers who are laid off or have their hours reduced.
- Difficulty finding a job: A recession can also make it more difficult for individuals to find new jobs, as the overall demand for labour tends to decline during a downturn. This can be especially challenging for workers who are laid off during a recession and are looking for new employment opportunities.
- The increased cost of living: A recession can also lead to higher costs of living, as prices for goods and services may rise due to reduced competition or other factors. This can make it more difficult for individuals to afford the things they need, such as food, housing, and healthcare.
Overall, a recession can be a difficult time for individuals, as it can lead to reduced income, difficulty finding work, and higher costs of living. However, most economies eventually recover from recessions and return to a period of growth, which can help to improve conditions for workers and consumers.